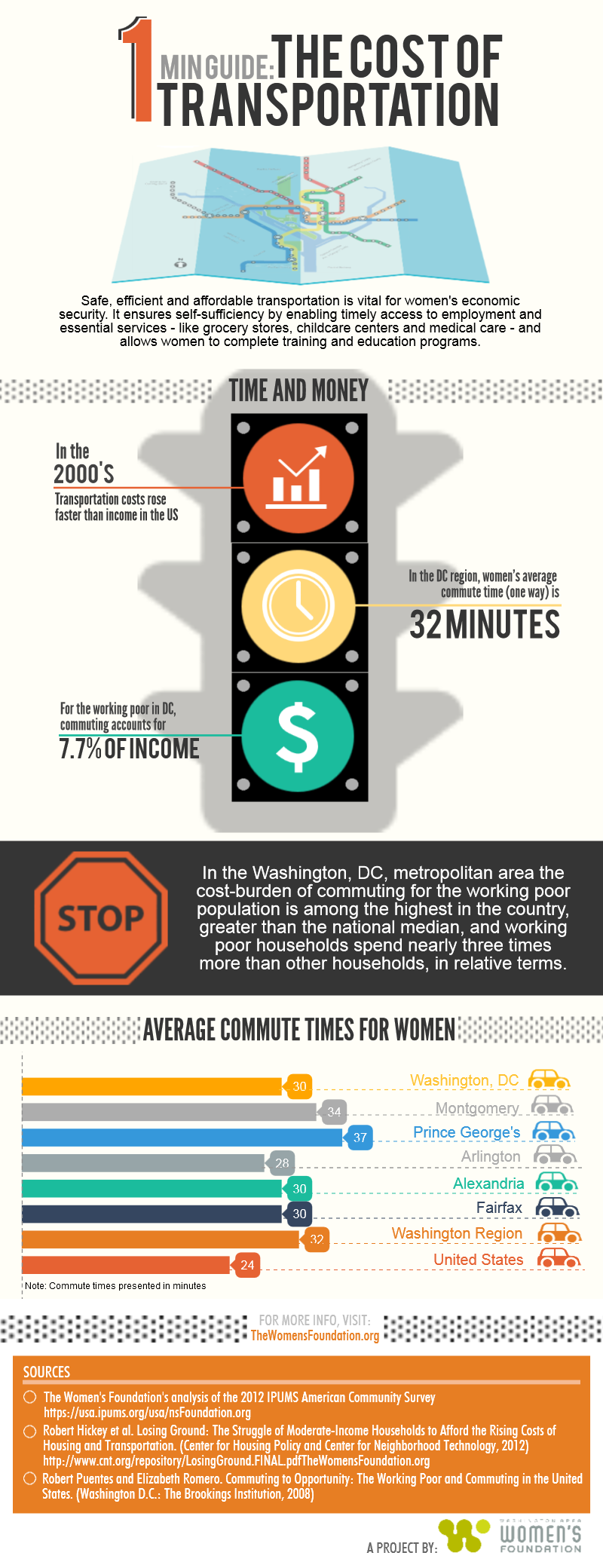
Safe, efficient and affordable transportation is vital for women’s economic security. It ensures self-sufficiency by enabling timely access to employment and essential services –like grocery stores, child care centers and medical care –and allowing women to complete training and education programs.
Finding affordable housing for a working family, particularly in our region, increasingly requires long commutes and high transportation costs. With the dispersion of jobs, services and other opportunities, it is not surprising that workers are spending more and more time commuting than ever before. Low-income housing, in underserved urban neighborhoods as well as in suburban areas, is located far from employment centers or disconnected from public transportation routes, preventing workers from getting to their destinations conveniently, efficiently and on time. In addition, urban revitalization projects in the capital region have brought an influx of affluent newcomers, usually displacing low-income residents to poorer neighborhoods that are further away and that lack public transportation infrastructure; not only making commutes longer, but also requiring more transfers and circuitous routing.
Many of the women participating in programs run by our Grantee Partners have reported that lack of reliable transportation is one of the most pervasive barriers to remaining employed or completing job training. A number of research studies underscore this experience. Findings suggest that the longer the commute, the less likely someone is to be employed, and they agree that lack of access to transportation is a major obstacle for workforce development.
Time spent commuting deserves attention from policymakers and grantmakers. Given the reasonable bandwidth of most people, long and complicated commutes are particularly expensive for those who have them, and can affect a program’s intake rates. Long commutes take away personal time that can’t be spent working, on education, running errands, or simply enjoying time with family or taking care of children. In 2012, women’s average commute time in the Washington Region was 32 minutes. In the same year, more than a quarter of female workers (27 percent) had commutes of 40 minutes each way and about 3 out of 100 female workers had “extreme commutes” of at least 90 minutes per trip, according to the American Community Survey.
Commuting costs
In addition to consuming time, commuting is also expensive in terms of dollars and cents. Transportation costs rose faster than income during the 2000s, increasing the burden these costs placed on already stretched budgets. For the working poor – those earning less than twice the federal poverty measure–these costs consume a larger portion of their earnings. In the Washington metropolitan area the cost-burden of commuting for this population is among the highest in the country, greater than the national median, and working poor households spend nearly three times more than other households, in relative terms. According to national data, transportation is the second largest expense for households: jointly with housing it accounts for more than one-half of all household spending.
What we are doing
Long and costly commutes discourage employment, leave workers with little to no time to spend with their families or to master the very skills needed for employment, and also leave them with fewer resources to accumulate savings and assets. Considering access to transportation is fundamental when The Women’s Foundation invests in programs working to improve the economic security of low-income women. We support efforts to link workforce development programs with transportation stipends, to ensure commuting to classes and meetings does not place an additional burden on or become a disincentive to women that would benefit from participating in our Grantee Partners’ programs. SOME, Year Up, and Goodwill are some of the many Grantee Partners providing some sort of transportation assistance as part of their education and training programs. This kind of assistance has proven to be a valuable approach in bridging the gap to meet low-income women’s needs, however, much more needs to be done to ensure transportation is not only accessible and affordable, but also safe and efficient. Considering transportation is crucial when developing policy recommendations and designing programs to lift women out of poverty so women can truly draw on and benefit from those initiatives.